Article Text
Abstract
Over the past decade, there have been major advances in Web 2.0 and Smartphone technologies. A recent systematic review carried out in 2013 has highlighted the lack of evidence base for existing mental health applications. Zhang et al have underscored how psychiatrists could be app-developers to negate the drawbacks of the current lack of evidence base for mental health applications. The new Mental Health Wellness application has been developed by Clinicians with experiences in mood disorder, and the aim of the app is to empower individuals to better manage their mental health conditions. The paper will illustrate the key features of the smartphone application and describes how a patient could make use of the application as a bridging tool between consults.
- Psychiatry
- mHealth
- Medical Apps
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Over the past decade, there have been major advances in Web 2.0 and Smartphone technologies. A recent systematic review carried out in 2013 has highlighted the lack of evidence base for existing mental health applications and have recommended that patients should keep a look out for applications that are evidenced based.1 Zhang et al2 have underscored how psychiatrists could be app-developers to negate the drawbacks of the current lack of evidence base for mental health application. To the best of our knowledge, there has not been an innovative app that helps patients deal with their mood condition and enforce compliance to medications. The new ‘Mental Health Wellness’ application has been developed by Clinicians with experience in mood disorders, and the aim of the app is to empower individuals to better manage their mental health conditions by ensuring compliance to medications (figures 1 and 2); and to enable them to rate their mood between consults (figure 3). In addition, given that psychological therapies do help patients in their recovery process, such resources are also included to help them deal with their illness. The application, in addition, enables patients to liaise with close contacts or their psychiatrists when they are in times of need. The application is currently available at the Apple iTunes store (see online supplementary video 1).3
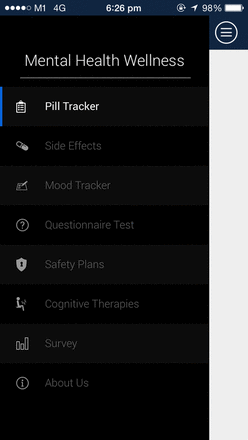
Application overview.
Demonstration of the visual pill reminder service.
Demonstration of the mood tracker function.
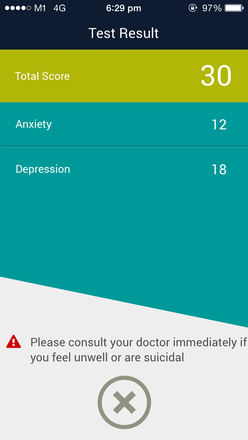
The application has been carefully designed, taking into consideration the needs of the patient. A patient newly diagnosed with depression can make use of the visual pill tracker to program in his/her medications, and be reminded to take his/her medications on a daily basis. In addition, in between the initial consultation to the next consultation, he/she could track his/her mood and the attending psychiatrist could discuss it during the next consult. The questionnaire test enables the psychiatrist to determine how the patient is doing objectively, using standardised measures, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9; figure 4). In the event that the patient is feeling extremely low in mood, he/she can make use of the safety plans feature to contact their loved ones. For patients who are improving, engaging in the therapies provided will help them restructure their thoughts.
Demonstration of the questionnaire feature.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Data
This web only file has been produced by the BMJ Publishing Group from an electronic file supplied by the author(s) and has not been edited for content.
- Data supplement 1 - Online video
Footnotes
Twitter Follow Melvyn Zhang at @melvynzhang
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.