Abstract
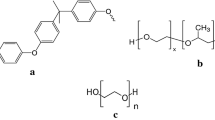
A detailed study on effects of additive (polyethylene glycol, PEG) in polysulfone (PSF) membrane was undertaken. The effects of molecular weight of PEG, its concentration, the nature of solvents, and thickness of casting solution were investigated. The cast membranes were characterized in terms of scanning electron microscopy for study of surface morphology, distilled water permeability, molecular weight cut-off (MWCO), contact angle, porosity, tensile strength. It was observed that more porous membranes were obtained using N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) as solvent compared to N, N- dimethylformamide (DMF). Controlling the concentration of PEG in the casting solution, one can get membrane of MWCO in the range of 10,000 to 70,000 while DMF was used as solvent. Hydrophilicity of the membranes increased with concentration and molecular weight of PEG. The average pore radius of the cast membranes was evaluated by two standard methods and the calculations led to reproducible results. Finally, the efficacy of the cast membranes for all the dosages of the PEG 400/PSF/DMF system was tested for filtration of turbid water of maximum turbidity 600 NTU. The feed and permeate were characterized using various properties, such as pH, conductivity, etc. It was observed that the cast membranes were effective for treatment of turbid water.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bungay PM, Lonsdale HK, de Pinho MN (eds) (1983) Synthetic Membranes: Science. Engineering and Applications, Reidel, Dordrecht
Porter MC (2005) Handbook of Industrial Membrane Technology. Crest Publishing House, New Delhi
Udel Polysulfone Design Guide, Version 2.1., Solvay Advanced Polymers LLC, (2002), 1.
Arthanareeswaran G, Mohan D, Rajenthirin M (2010) Preparation characterization and performance studies of UF membranes with polymeric additive. J Membr Sci 350:130
Chakraborty B, Ghosal AK, Purkait MK (2008) Effect of molecular weight of PEG on membrane morphology and transport properties. J Membr Sci 309:209
Han MJ, Nam ST (2002) Thermodynamic and rheological variation in polysulfone solution by PVP and its effect in the preparation of phase inversion membrane. J Membr Sci 202:55
Zheng QZ, Wang P, Yang YN (2006) Rheological and thermodynamic variation in polysulfone solution by PEG introduction and its effect on kinetics of membrane formation via phase-inversion process. J Membr Sci 279:230
Chen SH, Liou RM, Lai JY, Lai CL (2007) Effect of the polarity of additional solvent on membrane formation in polysulfone/N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone/water ternary system. J Eur Polym 43:3997
Zheng Q, Wang P, Yang YN, Cui DJ (2006) The relationship between porosity and kinetics parameter of membrane formation in PSF Ultrafiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 286:7
Tsai HA, Ruaan RC, Wang DM, Lai JY (2002) Effect of temperature an span series surfactant on the structure of polysulfone membranes. J Appl Polym Sci 86:166
Ma Y, Shi F, Ma J, Wu M, Zhang J, Gao C (2011) Effect of PEG additive on the morphology and performance of PSF UF membranes. Desalination 272:51
Han MJ, Nam ST (2002) Thermodynamic and Rheological variation in PSF solution by PVP and effects in the preparation of phase inversion membrane. J Membr Sci 202:56
Banerjee S, De S (2012) An analytical solution of Sherwood number in a stirred continuous cell during steady state ultra filtration. J Membr Sci 389:188
Li JF, Xu ZL, Yang H, Yu LY, Liu M (2009) Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface morphology and performance of micro porous PES membrane. Appl Surf Sci 255:4725
Hamid NAA, Ismail AF, Matsuura T, Zularism AW, Lau WJ, Yuliwati E, Abdullah MS (2011) Morphological and separation performance study of polysulfone/titanium dioxide(PSF/TiO2) ultrafiltration membranes for humic acid removal. Desalination 273:85
Singh S, Khulbe KC, Matsuura T, Ramamurthy P (1998) Membrane characterization by solute transport and atomic force microscopy. J Membr Sci 142:111
Zuo D-Y, Xu Y-Y, Xu W-L, Zou H-T (2008) The influence of PEG molecular weight on morphologies and properties of PVDF asymmetric membranes. Chinese J Polym Sci 26(4):405
Reuvers AJ, Van den Berg JWA, Smolders CA (1987) Formation of membranes by means of immersion precipitation. Part I.A. Model to describe mass transfer during immersion precipitation. J Membr Sci 34:45
Kim JH, Lee KH (1998) Effect of PEG additive on membrane formation by phase inversion. J Membr Sci 138:153
Mulder M (1991) Basic principles of membrane technology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 86.
Reuvers AJ, Smolders CA (1987) Formation of membranes by immersion precipitation part II: The mechanism of formation of membranes prepared from the system cellulose acetate-acetone- water. J Membr Sci 34:67
Strathmann U, Kock K, Amar P (1975) The formation mechanism of asymmetric membranes. Desalination 16:179
Rahimpour A, Madaeni SS (2007) Polyethersulfone (PES)/cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP) blend ultrafiltration membranes: Preparation, morphology, performance and antifouling properties. J Membr Sci 305:299
Rahimpour A, Madaeni SS, Mehdipour-Ataei S (2008) Synthesis of a novel poly(amide-imide) (PAI) and preparation and characterization of PAI blended polyethersulfone (PES) membranes. J Membr Sci 311:349
Vatanpour V, Madaeni SS, Khataee AR, Salehi E, Zinadini S, Monfared HA (2012) Ti02 embedded mixed matrix PES nanocomposite membranes: Influence of different sizes and types of nanoparticles on antifouling and performance. Desalination 292:19
Tiraferri A, Yip NY, Phillip WA, Schiffman JD, Elimelech M (2011) Relating performance of thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes to support layer formation and structure. J Membr Sci 367:340
Chakrabarty B, Ghosal AK, Purkait MK (2008) SEM analysis and gas permeability test to characterize PSf membrane prepared with PEG as additive. J Colloid Interface Sci 320:245
Lai JY, Lin FC, Wang CC, Wang DM (1996) Effect of nonsolvent additives on the porosity and morphology of asymmetric TPX membranes. J Membr Sci 118:49
Chou WL, Yu DG, Yang MC, Jou CH (2007) Effect of molecular weight and concentration of PEG additives on morphology and permeation performance of cellulose acetate hollow fibers. Sep Purif Technol 57:209
Boom RM, Wienk IM, Boomgaard TVD, Smolders CA (1992) Microstructures in phase inversion membranes: part 2. The role of a polymeric additive. J Membr Sci 73:277
Kim I-C, Lee K-H (2003) Effect of various additives on pore size of polysulfone membrane by phase-inversion process. J Appl Polym Sci 8(9):2562
Guan R, Dai H, Li C, Liu J, Xu J (2006) Effect of casting solvent on the morphology and performance of sulfonated polyethersulfone membranes. J Membr Sci 277:148
Dang HT, Amelot C, Rana D, Narbaitz RM, Matsuura T (2010) Performance of a newly developed hydrophilic additive blended with different ultrafiltration base polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 116:2205
McKelvey SA, Koros WJ (1996) Phase separation, vitrification, and the manifestation of macrovoids in polymeric asymmetric membranes. J Membr Sci 112:29
Amirilargani M, Sadrzadeh M, Mohammadi T (2010) Synthesis and characterization of polyethersulfone membranes. J Polym Res 17:363
Ping HT, Hua DS, Ying ZL (1991) The study of mechanism of organic additives action in the PS membranes casting solution. Desalination 83:343
Chun KY, Jang SH, Kim HS, Kim YW (2000) Effects of solvent on the pore formation in asymmetric 6FDA–4,4′ODA polyimide membrane: terms of thermodynamics, precipitation kinetics, and physical factors. J Membr Sci 169:197
Madaeni SS, Rahimpour A (2005) Effect of type of solvent and non-solvents on morphology and performance of polysulfone and polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes for milk concentration. Polym Adv Technol 16:7
Amirilargani M, Mohammadi T (2009) Effects of PEG on morphology and permeation properties of Polyethersulfone membranes. Sep Sci Technol 44:3854
Madaeni SS, Taheri AH (2011) Effect of Casting Solution on Morphology and Performance of PVDF Microfiltration Membranes. Chem Eng Technol 34:1328
Choi JH, Jegal J, Kim WN (2006) Fabrication and characterization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polymer blend membranes. J Membr Sci 284:406
Albrecht W, Weigel T, Schossig-Tiedemann M, Kneifel K, Peinemann KN, Paul D (2001) Formation of hollow fiber membranes from poly(ether imide) at wet phase inversion using binary mixtures of solvents for the preparation of the dope. J Membr Sci 192:217–230
Chen J, Spear SK, Huddleston JG, Rogers RD (2005) Polyethylene glycol and solutions of polyethylene glycol as green reaction media. Green Chem 7:64–82
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, S.R., De, S. Role of polyethylene glycol with different solvents for tailor-made polysulfone membranes. J Polym Res 20, 179 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0179-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0179-4