Abstract
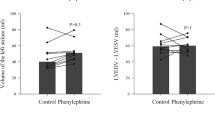
Objective. We tested the hypothesis that peripheral vasodilation has an effect on arterial oxygen saturation measurements by pulse oximetry, independent of temperature. Methods. Study 1 compared finger arterial oxygen saturation values (SpO2), before and after peripheral vasoconstriction while temperature was kept constant. This was achieved by administering dexmedetomidine (peripheral vasoconstrictor) to 16 volunteers given general anesthesia. Study 2 compared SpO2 before and after peripheral vasodilation (brachial plexus block) in a neurally denervated left hand and a neurally innervated right hand in ten awake volunteers. In both studies measurements were also made of finger blood volume (an indicator of vasoconstriction) by photoplethysmographic determination of light transmission through a finger (LTF), finger temperature and of hemodynamic variables. Results. In Study 1, systolic blood pressure, SpO2 and LTF values increased (vasoconstriction) during dexmedetomidine infusion, (P<0.0001 for all) while there were no changes in finger temperature. In Study 2, in the left hand (axillary block), temperature increased by 1.9 ± 1.6 °C (P=0.004), SpO2 decreased by 2.5 ± 1.0 % (P<0.0001) and LTF values decreased (vasodilation) by 42 ± 8 % (P<0.0001) after axillary block. Simultaneously, the axillary block did not induce any changes in temperature, SpO2 or LTF values in the neurally innervated right hand. Conclusions. Our results demonstrate that finger pulse oximeter SpO2 measurements can be affected by peripheral vascular tone independent of temperature. The mechanism for this effect remains speculative and unproven.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JM, Arakawa K, Benson KT, Fox DK. Pulse oximetry and circulatory kinetics associated with pulse volume amplitude measured by photoelectric plethysmography. Anesth Analg 1986; 65: 1333–1339.
Kelleher JF, Ruff RH. The penumbra effect: Vasomotion-dependent pulse oximeter artifact due to probe malposition. Anesthesiology 1989; 71: 787–791.
Sessler Dl, McGuire J, Hynson J, Moayeri A, Heier T. Thermoregulatory vasoconstriction during isoflurane anesthesia minimally decreases cutaneous heat loss. Anesthesiology 1992; 76: 670–675.
Hynson JM, Sessler Dl, Belani K, Washington D, McGuire J, Merrifield B, Schroeder M, Moayeri A, Crankshaw D, Hudson S. Thermoregulatory vasoconstriction during propofol/nitrous oxide anesthesia in humans: Threshold and oxyhemoglobin saturation. Anesth Analg 1992; 75: 947–952.
Schramm WM, Bartunek A, Gilly H. Effect of local limb temperature on pulse oximetry and the plethysmographic pulse wave. Int J Clin Monit Comput 1997; 14: 17–22.
Sami HM, Kleinman BS, Lonchyna VA. Central venous pulsations associated with a falsely low oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry. J Clin Monit 1991; 7: 309–312.
Nellcor N. 200 Service Manual, Hayward, CA. 1989.
Talke P, Stapelfeldt C, Lobo E, Brown R, Scheinin M, Snapir A. Alpha-2B adrenoceptor polymorphism and peripheral vasoconstriction. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2005; 15: 357–363.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talke, P., Stapelfeldt, C. Effect of Peripheral Vasoconstriction on Pulse Oximetry. J Clin Monit Comput 20, 305–309 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-006-9022-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-006-9022-3